
How stress can trigger paranoia is unclear.
Stress reaction – some studies have found that paranoia is more common in people who have experienced severe and ongoing stress – for example, prisoners of war. Traumatic life events – for example, abuse in childhood may distort the way a person thinks and feels throughout life. The causes of this possible disorder are unknown. This leads some researchers to believe that paranoia may be a biochemical disorder of the brain. Certain drugs such as cocaine, marijuana and amphetamines alter brain chemistry and can bring on paranoid thoughts, feelings and behaviours. Brain chemistry – brain chemicals (neurotransmitters) form the basis of thoughts and feelings. It is also unclear whether genetic predisposition to paranoia – if it exists – is inherited or not. Some studies suggest a genetic link while others don’t. Genes – research is scanty and inconclusive. 
The causes of paranoia are unclear and depend on the condition with which it is associated. A person with paranoid schizophrenia often finds the world confusing and functions poorly without treatment. Hallucinations, especially bizarre ones, are also common to the condition. It is characterised by strange delusions, such as believing that one’s thoughts are being broadcast over the radio. Paranoid schizophrenia – considered the most severe type.In another case, a person may imagine they have a terrible illness, despite repeated reassurance from doctors.
#Paranoid meaning movie
Stalking can be the result of delusional (paranoid) disorder – for example, the person believes they are in a relationship with a movie star they have never met. For example, a person who has a delusion of persecution believes that other people are spying on them or plotting to harm them in some way.
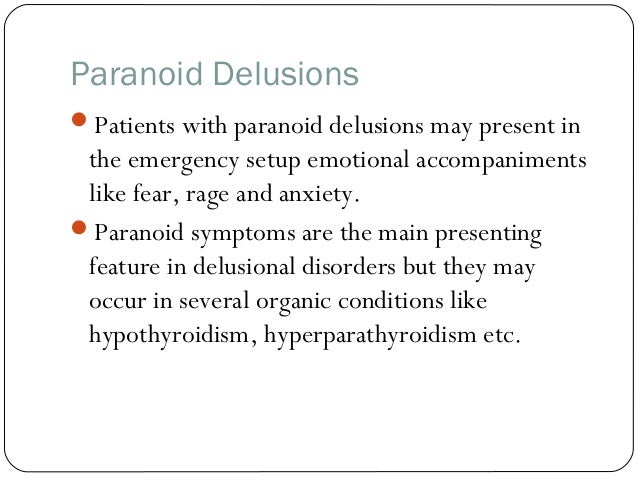
The person’s behaviour depends on which delusion they have.
Delusional (paranoid) disorder – characterised by the dominance of one delusion (false belief) without any other sign of mental illness. The attitudes and behaviours associated with this disorder, when they become obvious, are often discovered to have been present for much of the person’s life. Most people with paranoid personality disorder function well despite their mistrust of the world. Paranoid personality disorder – considered the mildest type. Paranoia is associated with three principal conditions: Believe in unfounded ‘conspiracy theories’. Consider the world to be a place of constant threat. Be overly suspicious – for example, think that other people are lying or scheming to cheat them. Assume that people are talking ill of them behind their back. Find it difficult, if not impossible, to ‘forgive and forget’. Be hostile, aggressive and argumentative. Assign harmful meanings to other people’s remarks. They depend on the cause but, generally, a person who is paranoid may: Paranoid symptoms may range from mild to severe. Treatment depends on the condition diagnosed as its cause, and may include treatment by psychological therapy or medication. The cause of paranoia is unknown but genetics are thought to play a role. Paranoia may be a symptom of a number of conditions, including paranoid personality disorder, delusional (paranoid) disorder and schizophrenia. This unfounded mistrust of others can make it difficult for a person with paranoia to function socially or have close relationships. 
Paranoia is the irrational and persistent feeling that people are ‘out to get you’ or that you are the subject of persistent, intrusive attention by others.







 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
